Introduction
Recent developments in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have enabled significant strides in identifying human emotions through body language analysis. A team of researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the University of Duisburg-Essen has developed an AI model capable of accurately identifying the emotions of tennis players during matches. This advancement opens up new possibilities not only for sports but also for other applications, while also raising important ethical issues.
The Study and the Technology Used
Methodology and Data
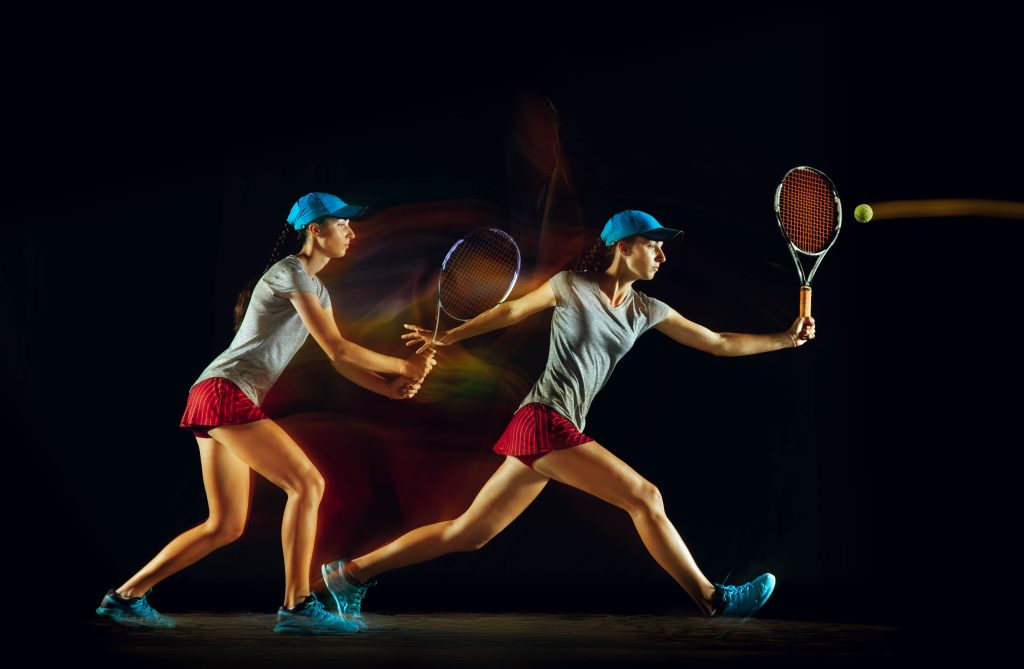
The core of the study, titled “Recognizing Affective States from Expressive Behavior of Tennis Players Using Convolutional Neural Networks,” is based on the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs). These networks were trained on videos of real tennis matches, focusing on players’ body language during key moments, such as winning or losing a point. Researchers recorded video sequences of 15 tennis players, analyzing expressive signals such as lowered heads, raised arms in celebration, and walking speed.
Model Accuracy
The developed model achieved an accuracy of 68.9% in recognizing emotional states, a result comparable to and sometimes exceeding human evaluations and other automated methods. “Our model can identify affective states with an accuracy of up to 68.9%, which is comparable to and sometimes even better than assessments made by human observers and previous automated methods,” said Professor Darko Jekauc of KIT.
Results and Interpretations
Recognition of Negative Emotions
One of the most interesting aspects of the study is the AI’s greater ability to recognize negative emotions compared to positive ones. This phenomenon was also observed in human observers. “The reason could be that negative emotions are easier to identify because they are expressed in more obvious ways,” Jekauc explained. Psychological theories suggest that humans are evolutionarily predisposed to more easily perceive negative emotional expressions, as they are crucial for social cohesion and conflict resolution.
Future Implications
Sports and Training
The accuracy of emotional recognition through AI could revolutionize sports training. Coaches could use this data to improve team dynamics, optimize player performance, and prevent burnout. The ability to quickly identify emotional states could lead to timely and personalized interventions, enhancing athletes’ well-being.
Applications in Other Sectors
Beyond sports, the potential applications of this technology are vast. In healthcare, it could be used to monitor patients’ emotional conditions, providing timely support. In education, it could help teachers better understand students’ emotions, adapting teaching strategies accordingly. Customer service and automotive safety could also benefit from reliable early diagnosis of emotional states.
Ethical Issues
Privacy and Data Use
Despite the promising applications, the use of AI for emotion recognition raises important ethical issues. The privacy of subjects is a primary concern, as is the potential misuse of collected data. “Our study adhered strictly to existing ethical guidelines and data protection regulations. And in view of future applications of such technology in practice, it will be essential to clarify ethical and legal issues in advance,” Jekauc emphasized.
Conclusion
The study conducted by KIT and the University of Duisburg-Essen represents a significant advance in emotion recognition through AI. With an accuracy of 68.9%, this technology has the potential to revolutionize not only the sports world but also many other areas. However, it is crucial to address ethical issues related to privacy and data use to ensure that these tools are used responsibly and beneficially.