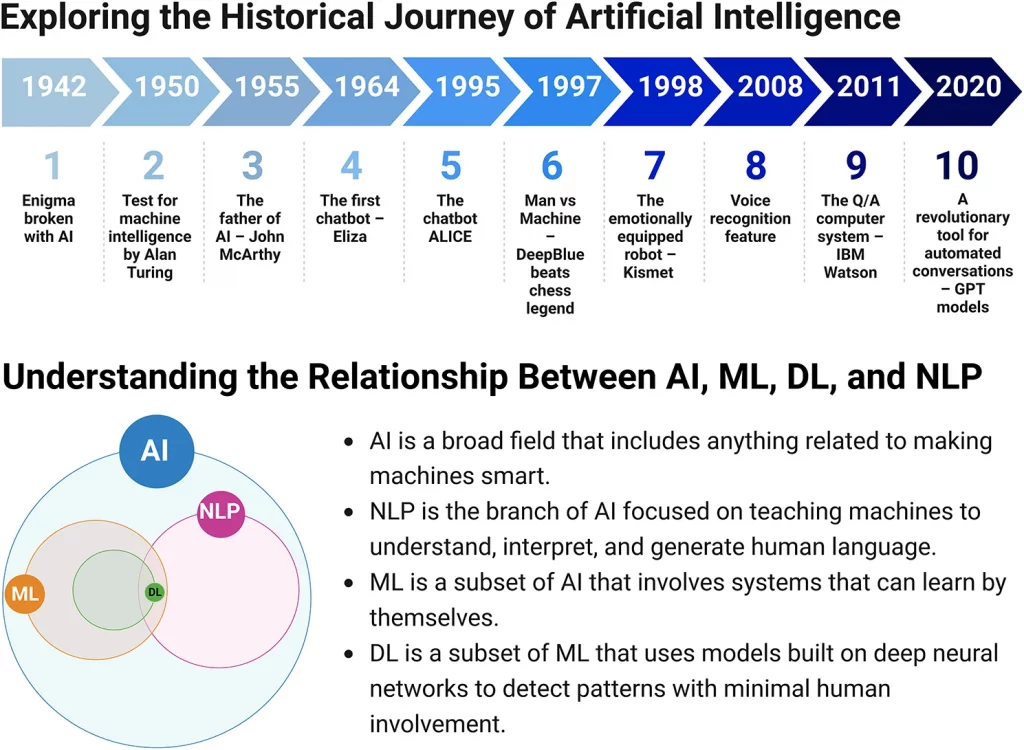
The modern healthcare system faces immense challenges. An aging global population, the increase in chronic diseases, the increasing complexity of care and the constant pressure on resources and healthcare workers create a challenging picture. It is a world where every second counts and where the ability to manage enormous quantities of information can make the difference between early and late diagnosis, between effective and less suitable treatment. But precisely in this complex scenario, a new, transformative force is emerging, with the potential to rewrite the rules of medical care: Artificial Intelligence, or AI.
AI is no longer confined to research labs or science fiction films. It is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field of computer science that aims to create machines capable of performing tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. Techniques like Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are the tools with which AI is starting to penetrate every industry, and healthcare is at the forefront of this revolution. It’s not simply about automating mundane tasks, but about developing technologies that can improve patient care in previously unthinkable ways.
Rewriting the Diagnosis: Unprecedented Speed and Accuracy
One of the fields where AI is already demonstrating transformative potential is disease diagnosis. Traditional diagnostic methods, while refined by human experience, can be costly in terms of time and resources, and sometimes prone to errors. AI, on the other hand, has an extraordinary ability to analyze enormous data sets – medical images, laboratory results, patient histories – and identify patterns that would escape even the most expert eye.
Imagine the diagnosis of cancer. Studies conducted on mammograms have shown how AI systems can significantly reduce both false positives (indicating a non-existent cancer) and false negatives (not detecting a present cancer), improving sensitivity, especially in early diagnosis. Another exciting example comes from dermatology, where deep learning algorithms, in particular Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), have demonstrated remarkable accuracy in diagnosing melanoma starting from images of skin lesions, sometimes exceeding the performance of dermatologists themselves.
But it’s not just cancer. AI is proving invaluable in detecting diabetic retinopathy from eye images, analyzing electrocardiograms to detect cardiac abnormalities, predicting cardiovascular risk factors, and even diagnosing pneumonia from high-sensitivity chest x-rays. Even in clinical testing laboratories, AI is revolutionizing the identification and quantification of microorganisms, the classification of Gram stains, and even the rapid and cost-effective detection of malaria in unstained blood samples. This means faster diagnoses, reduced costs and, above all, greater accuracy for patients.
Tailored Treatments: The Dawn of Personalized Medicine
AI doesn’t stop at diagnosis; its impact on treatment is perhaps even more profound, opening the door to truly personalized medicine. Today we know that each patient is unique, with genetic characteristics, lifestyles and responses to drugs that vary enormously. Adapting therapy to individual specificities is the goal of precision medicine, and AI is the ideal tool to achieve it.
AI algorithms can analyze complex data, including genomic profiles and clinical data, to predict an individual patient’s response to specific therapies. Let’s think about chemotherapy: being able to predict with good precision whether a patient will respond to a certain drug can avoid ineffective treatments, reduce unnecessary side effects and immediately direct towards the most promising therapeutic strategy. Similarly, AI is proving effective in predicting response to specific classes of antidepressants based on analysis of electronic health records.
Another crucial aspect is the optimization of drug dosage, vital especially for those medicines with a narrow therapeutic index, where a slightly incorrect dosage can lead to ineffectiveness or toxicity. AI can predict drug-drug interactions and identify patients at high risk of adverse reactions. AI-based systems, such as CURATE.AI, have been tested to dynamically modulate chemotherapy doses based on individual patient response, showing potential benefits in terms of reducing doses and improving response rates and duration. This is not just a scientific advance; it is a promise of safer, more effective and tailor-made therapies for each individual.
Managing Health on a Large Scale and in Critical Situations
AI doesn’t just improve individual patient care, it has the ability to influence the health of entire populations. Predictive analytics, powered by AI and Machine Learning, allows for early identification of individuals or groups at risk of developing chronic diseases or being readmitted to hospital after discharge. This allows healthcare organizations to intervene in a targeted and proactive way, offering support and prevention to those who need it most, with the aim of improving clinical outcomes and reducing overall costs.
A concrete example comes from Saudi Arabia, where a big data analysis tool based on Twitter data, called Sehaa, is used to detect the onset of diseases at a population level and guide health awareness campaigns in the most affected geographic areas. These systems can even automate tasks like patient contact and care coordination, freeing up valuable time for healthcare workers.
Even in high-pressure environments like emergency rooms, AI integration is seen as a necessity. AI algorithms can analyze patient data to assist in triage, quickly identifying the most urgent cases and reducing wait times, a critical factor in emergency situations. AI-based decision support systems can offer real-time suggestions to doctors and nurses, helping them make faster and more informed diagnostic and treatment decisions, helping to reduce the risk of diagnostic errors, which can have serious consequences. AI can also optimize resource allocation by predicting patient demand at different times.
AI at the Patient’s Side: Virtual Assistance and Mental Support
AI’s most direct and personal impact on patients’ lives occurs at the point of care. Virtual healthcare assistants, in the form of chatbots or phone applications, are becoming digital companions for many people. These AI-powered tools can help patients describe their symptoms to identify possible problems, provide general medical advice, send medication reminders, facilitate appointment booking, and even monitor vital signs remotely. By integrating these tools, it is possible to reduce the workload of healthcare personnel and make care more accessible, especially for those who have difficulty traveling or live far from medical centers.
One particularly promising area is mental health support. AI has the potential to revolutionize access and personalization of psychiatric care, which often suffers from long waiting lists and social stigma. AI-based applications can aid in early diagnosis, offer personalized treatment pathways, and continuously monitor patient progress. Studies on apps like Woebot have demonstrated their effectiveness in supporting people with substance use disorders, depression and anxiety, offering 24-hour support. While they cannot replace the human therapeutic relationship, these digital tools can complement and make treatment more accessible.
Patient education also benefits enormously from AI. Intelligent chatbots can provide personalized, interactive information to patients and caregivers about diagnoses, treatment options and preventive measures, improving understanding of their condition and adherence to therapies. They can also adapt the language complexity of educational materials to different reading levels, ensuring that crucial information is accessible to all. Giving patients the tools to better understand and manage their health is a fundamental step towards more effective care.
Genomics and Beyond: Unlocking the Secrets of DNA with AI
The fusion between AI and genomic data analysis is an area with enormous, almost science fiction potential, but one that is becoming reality. AI can work with massive genetic datasets to monitor the evolution of emerging health threats, as happened with COVID-19. But, even more fascinating, it can reveal genetic markers associated with increased susceptibility to specific diseases.
Machine learning algorithms are capable of identifying complex patterns in genetic variations linked to disease susceptibility, patterns that are too intricate to be detected with traditional statistical methods. This allows for a much more precise prediction of disease risk, based on individual genetic heritage. This combination of high-throughput genomic sequencing and AI technologies is critical to accelerating personalized medicine and drug discovery, helping to identify new therapeutic targets and predict drug toxicity before they are administered to patients. It’s as if AI is helping to read and interpret the book of life written in our DNA, unlocking secrets to better health and more targeted treatments.
Human Necessity and the Challenges to Face
Despite the exciting potential, it is critical to recognize that AI is not a magic panacea. Its integration into clinical practice presents significant challenges that require careful consideration and proactive management. The quality of the medical data on which the algorithms are trained is crucial; incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to unreliable and even harmful results.
Data privacy and security are primary concerns. The enormous amount of sensitive information that AI systems handle makes them attractive targets for cyberattacks, with enormous risks for patients. It is imperative to develop and implement robust cybersecurity strategies.
Another inherent challenge is bias. AI algorithms are trained on historical data that can reflect and even amplify existing human biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes for certain patient populations. Constant vigilance and development of methods to mitigate these biases is required. There is also the risk of “hallucination,” where AI generates data or analyzes that appear realistic but are completely fabricated.
Perhaps the most important consideration is the need for human expertise and involvement. AI is a powerful tool, but the final decision always rests with the healthcare professional. AI does not replace clinical judgment, empathy, experience and the relationship of trust between patient and doctor. This trusting relationship is vital to the acceptance and success of AI-based healthcare systems. Public perception on the use of AI in healthcare is still mixed; while many are willing to use AI tools for specific tasks, most still prefer human intervention for complex or sensitive issues. Building trust requires transparency and tangible results.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort. Collaboration between AI developers, clinicians, researchers, regulators and patients is essential to ensure the development of robust, ethical and truly useful systems. Regulation is still in its infancy, but international bodies are working to define clear guidelines. Additionally, educating future and current healthcare professionals about AI is critical to ensure they are equipped to effectively use these emerging technologies and understand their limitations. Medical schools are encouraged to incorporate AI into their curricula.
Looking to the Future: A Partner for Care
Artificial Intelligence is opening an exciting chapter in the history of medicine. From improving the accuracy of diagnosis and personalizing treatments, to optimizing public health management and making care more accessible to patients, its potential to revolutionize healthcare is immense. It is not a force that competes with human experience, but a valuable ally that can enhance it, free up precious time and lead to better outcomes for patients.
For this promise to be fully realized, it is crucial to face the challenges responsibly, ensuring data quality, privacy, equity and harmonious integration with healthcare personnel. Continuous collaboration, research and ethical development are the pillars on which to build the future of AI-enhanced medicine.
The ultimate goal is not a healthcare system run by machines, but one in which the wisdom, experience and empathy of healthcare professionals is amplified by the speed, precision and analytical capabilities of AI. It’s a future where technology and humanity work together to improve the quality of life and make healthcare more effective, efficient and equitable for all. It’s an exciting journey, and Artificial Intelligence is an essential travel companion.